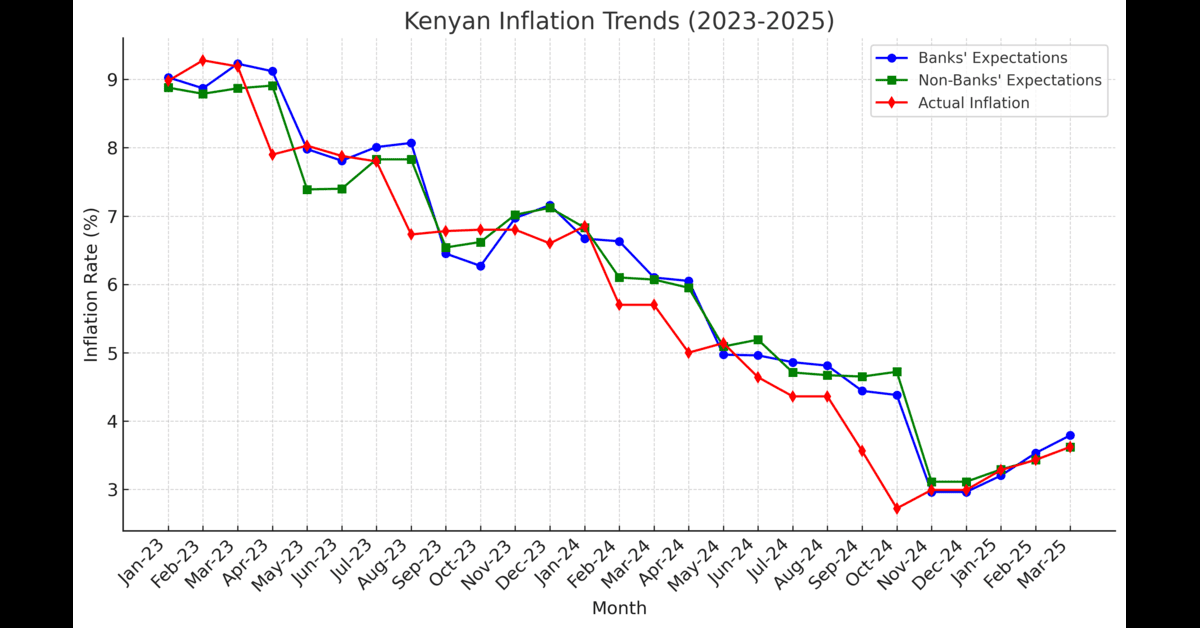
Inflation continues to reshape the banking industry, influencing profits, costs, and overall financial stability. As inflation rates fluctuate, banks face new challenges in maintaining profitability while navigating shifts in interest rates and operational expenses.
Inflation and Its Impact on Bank Revenues
Banks generate revenue from interest and non-interest income. Inflation affects both revenue streams in different ways. Interest income typically increases when inflation leads to higher interest rates interest income typically increases. Higher borrowing costs result in lower loan demand and a greater risk of borrowers defaulting.
Non-interest income, which includes fees from services, trading, and other financial activities, is more directly impacted by inflation. Rising salaries, rent, and operational expenses can erode earnings, especially for banks with high exposure to these costs.
Inflation’s Role in Bank Expenses
The cost of doing business rises with inflation. Banks must pay higher wages to retain employees and manage increasing expenses related to operations and compliance. Additionally, procurement costs for essential banking technologies and services also surge. If these expenses grow faster than revenue, bank profitability weakens.

Inflation and Interest Rate Policies
Inflation directly influences central bank policies. Central banks often raise interest rates to curb inflation, which can benefit banks in the short term by widening net interest margins. Persistently high interest rates discourage borrowing, slow economic growth, and increase the risk of loan defaults. These defaults then negatively impact banks.
Related Article: CBK Interest Cuts: What To Know Now!
Vulnerabilities in the Banking Sector
Not all banks experience inflation in the same way. According to recent studies, banks heavily relying on non-interest income or those with high operational costs are more vulnerable to inflationary pressures. Emerging market banks, in particular, face higher risks due to economic volatility and less predictable policy responses.
What Is Next for Banks?
While inflation can create opportunities for banks through higher interest income, it also introduces risks that can erode profitability. Effective risk management, strategic pricing, and cost control measures are essential for banks to remain profitable in an inflationary environment. As inflation trends evolve, banks must adapt to maintain financial stability and growth.